1. What is PHA?
PHA is a natural polymer, produced by bacteria using starch or vegetable oil.
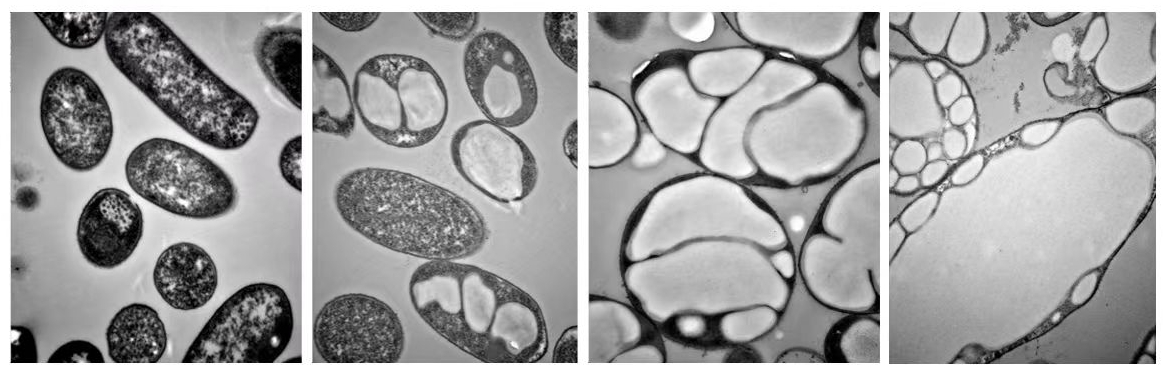
2. How it is made?
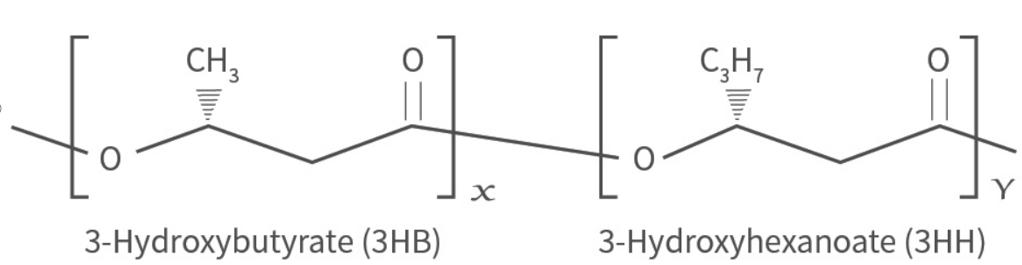
3. What is the molecular structure?
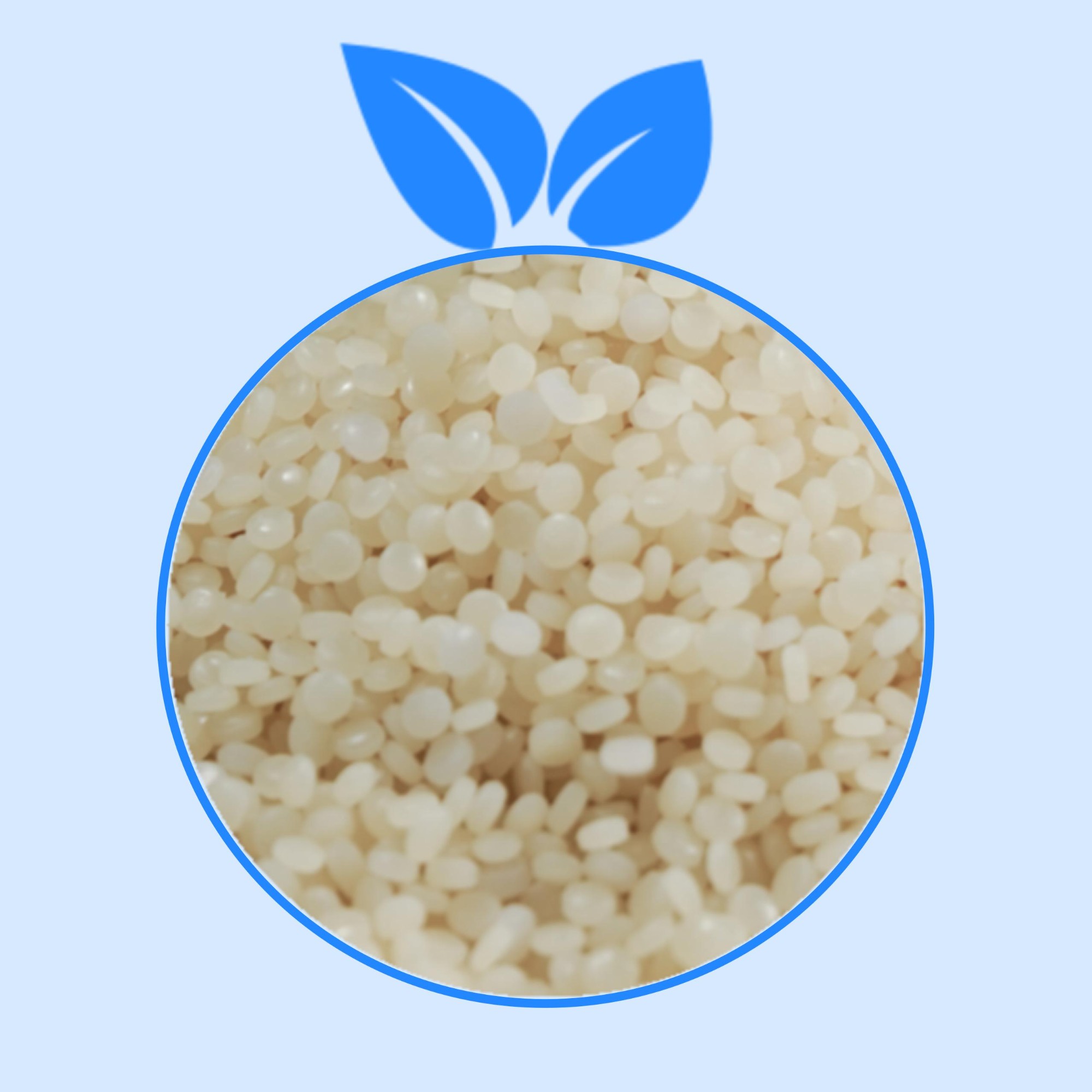
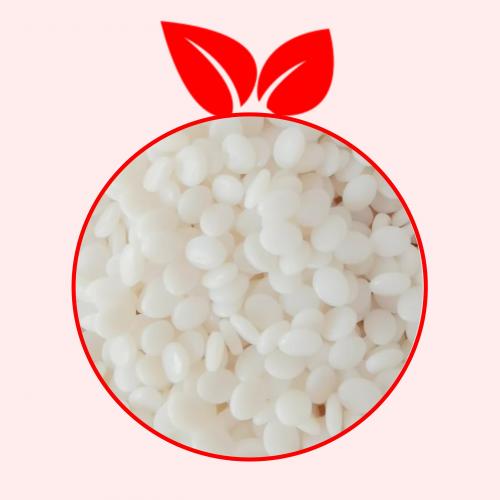
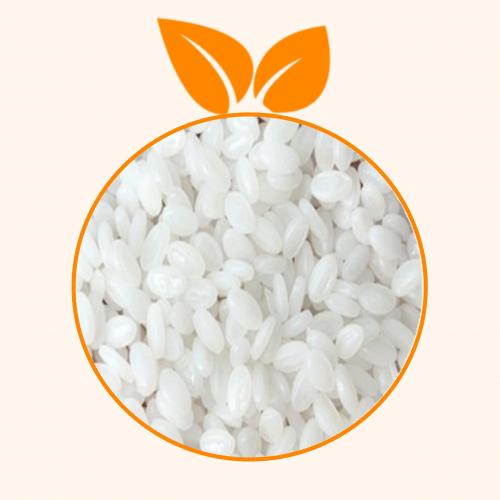
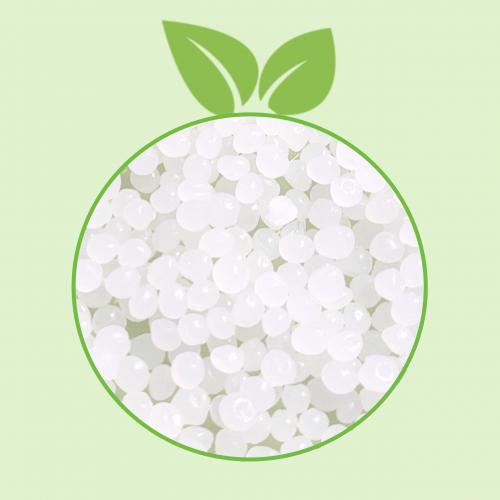
4. Product shape and photo

Translucent pellets and natural powder
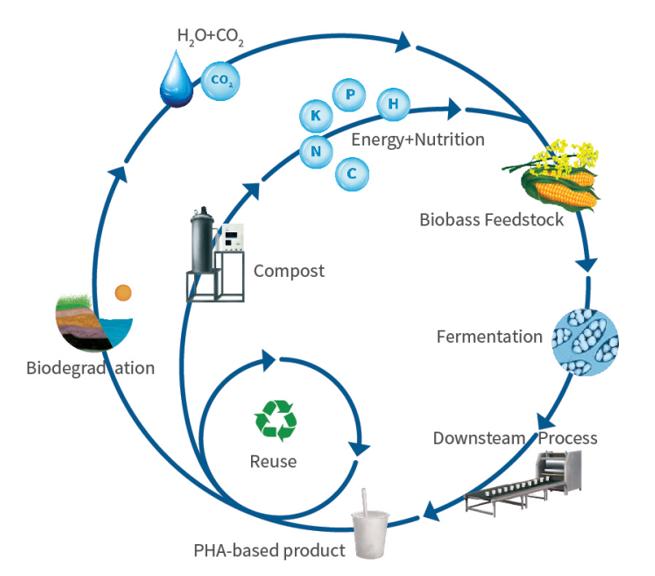
5. Life cycle
6. Grades and specifications
Properties | Y1000P-PHBV | Y3000P-PHB | Bluepha-PHBH |
Density(g/cm³) | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.20±0.02 |
Melt Flow Index | 5-18 | 5-18 | 3±2 |
Melting Point(℃) | - | - | 148±2 |
Glass Transition Temperature(℃) | - | - | 3±3 |
Yield Stress ( MPa) | 31-36 | 31-36 | |
Tensile Strength (MPa) | 39 | 38 | ≥30 |
Elongation at Break (%) | 3.8 | 3.2 | ≤5 |
Young’s Modulus(MPa) | 1600-2100 | 1600-2100 | ≥800 |
Flexural Modulus (MPa) | 2200-2900 | 2500-3200 | ≥1700 |
Vicat Softening Temperature (℃) | 166 | 164 | - |
Izod Impact (J/m) | 55-70 | 50-65 | - |
Charpy Impact Strength(kJ/㎡) | - | - | ≤3 |
Heat Deflection Temperature (℃) | 157-165 | 135-145 | ≥100 |
DSC Melting Point (℃) | 175-180 | 175-180 | - |
7. Features
100% biobased
100% plant sourced
physical properties are similar to fossil-based plastics
Heat resistant
Heat sealability
Hydrolysis stablity
Good barrier properties
Eco-friendly
Compostable and Biodegradable
Low carbon footprint
Food contact safety
Toxic free
8. Applications
Injection I Extrusion I Thermoforming I Blown film I Casting film I Lamination I 3D printing I Fiber/Non-woven
9. Compostability
Home compostable I Industrial compostable I Marine biodegradable I Water biodegradable I Soil biodegradable
10. Certificates











